SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are used to fight against spam. To ensure your emails are delivered properly to the inbox & you won’t have issues with e-mail spoofing, you need to setup SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records for your domain.
What is SPF?
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) is a way to stop hackers and spammers from sending out spoofing emails using your email address.
Don’t they need my email password to do that? No. A password is only needed to see what emails an email address has received. Think about your mailbox (hopefully secured with a lock and key). Only a person with the right key (or password) can access your mailbox and read the letters inside. However, anyone could send a letter pretending to be from you, and write your address in the return field. Email is exactly the same in this regard.
How does SPF stop that? Think of SPF as your secretary. Whenever someone gets an email with your name on it, they call your secretary and ask them if that email came from you. If not, whoever receives the email will throw it in the junk.
In more technical terms, an SPF record lists IP addresses and domain names of the servers that are allowed to send email from your email address. When an email is sent, the receiving server records what IP address the email came from. It checks if that IP matches one in the SPF record, and if not the email is rejected. Potential hackers would need a password both to edit your SPF and to send email from servers you’ve authorized, so this prevents email spoofing.
What is DKIM?
DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail) is an email authentication technique that allows the receiver to check that an email was sent and authorized by the correct email account, and wasn’t modified in transit.
This is done by generating a digital signature for the email. This DKIM signature is encrypted and added to the message. If the email is altered between the time that it is sent and received, the signature will no longer match. The email server receiving your email can check the signature in the email, and reject the email if it doesn’t contain exactly the right signature.
As an example, if you send a letter containing your will to your lawyer, you may be worried that the letter could be could be intercepted and changed before it is delivered. To prevent this, you could fold and scrunch up the letter in a way that will produce a very specific pattern of creases that’s impossible to recreate exactly. You could then send a secret communication to your lawyer describing the pattern in its finest details. If anyone was to open up the letter and make modifications, this would alter the pattern. When your lawyer receives the email, they would check to see if the pattern perfectly matches your description, and would reject the letter if it doesn’t.
What is DMARC?
While it’s a complex tool, the basic function of DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) is to answer the question: “What happens if emails I send out fail an SPF or DKIM check?” DMARC tells a server whether to accept or reject emails that fail SPF/DKIM checks, and allows you to specify how you are notified of those failures.
Do I need it? DMARC does not provide a security increase, as unlike SPF and DKIM it does not provide a way to authenticate your mail. However, DMARC is still a very useful tool for two reasons. Firstly, when a hacker spoofs your email they typically do this for a number of days/weeks, and the recipient’s server will send you bouncebacks of every spoofed email sent. These come through as legitimate emails which can fill up your mailbox. DMARC provides options for how these bouncebacks are handled. Secondly, if you’re sending important emails out, a DMARC record can let you know if the email didn’t reach one of its intended recipients.
How to Setup SPF & DKIM Records
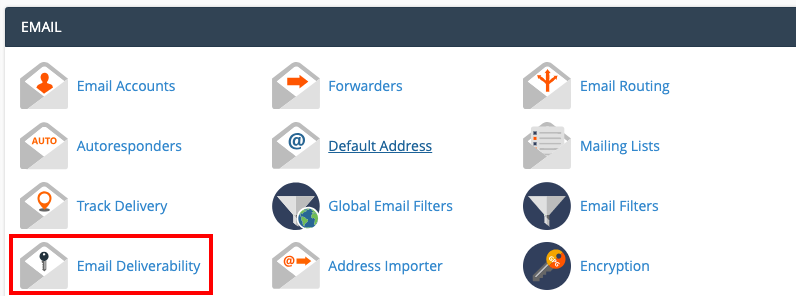
Step 1: Log into cPanel and click on Email Deliverability.
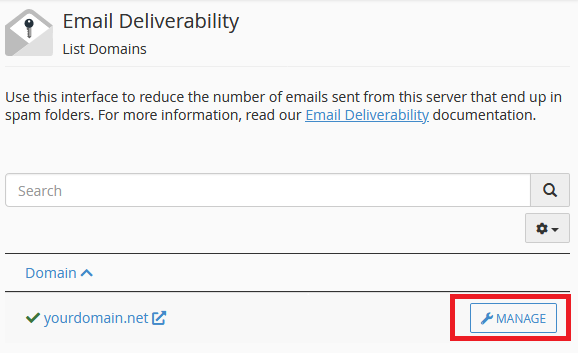
Step 2: Find the domain you want to enable SPF and DKIM for, and click on Manage.
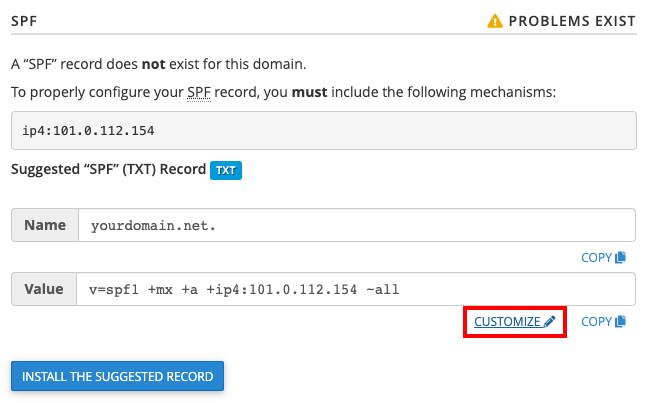
Step 3: Underneath the heading DKIM, click on Install the Suggested Record.
Step 4: After the DKIM record is installed, underneath the heading of SPF, click on Customize.
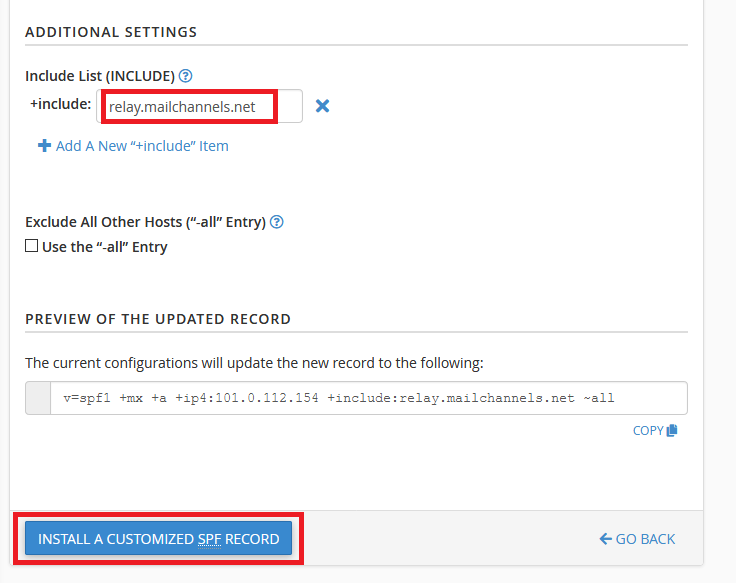
Step 6: Under the heading Additional Settings:
(1) Include “relay.mailchannels.net“. If you have been asked to add other “+include” items like ‘_spf.google.com’, use the ‘Add a New +include Item‘ option.
(2) Click on Install a Customized SPF Record.
Now SPF & DKIM has been setup.
How to Enable DMRAC Record
Before you add a DMARC record, make sure you have enabled SPF and DKIM.
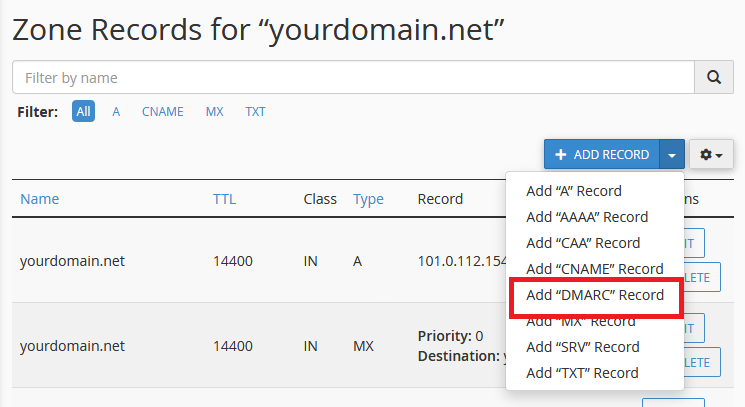
Step 1: Log into cPanel and click on Zone Editor.
Step 2: Click Manage for the domain you want to add the DMARC to:
Step 3: Click +Add Record then Add DMARC Record.
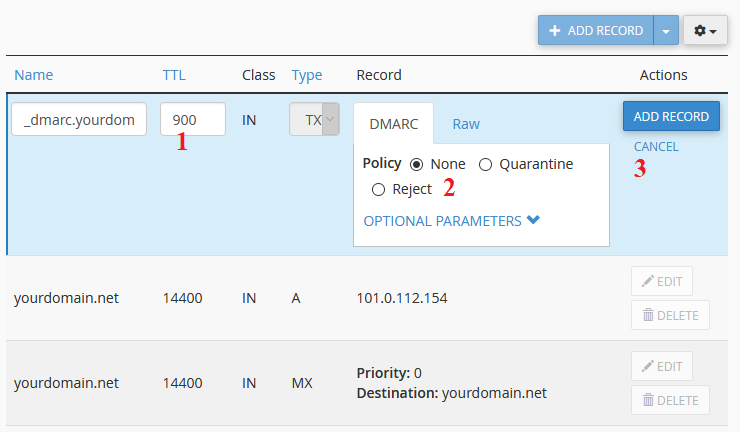
Step 4: Confirm the DMARC settings:
(1) Set the TTL to 900.
(2) Select how you want the DMARC record to act:
None: Treat failed SPF emails as normal.
Quarantine: Send failed SPF emails to a SPAM/Junk folder.
Reject: Reject failed SPF emails completely.
(3) Click Add Record.
How to Configure Advanced DMARC Record
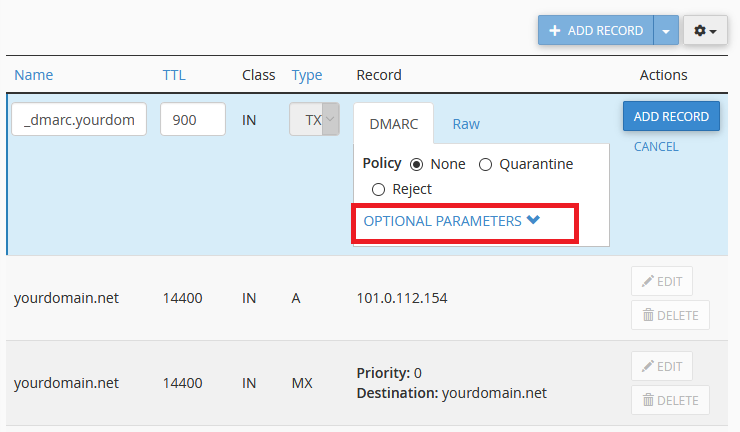
Add a DMARC record as you would in the basic guide, but instead of clicking Add Record, click Optional Parameters first. Once DMARC configuration is complete, click Add Record.
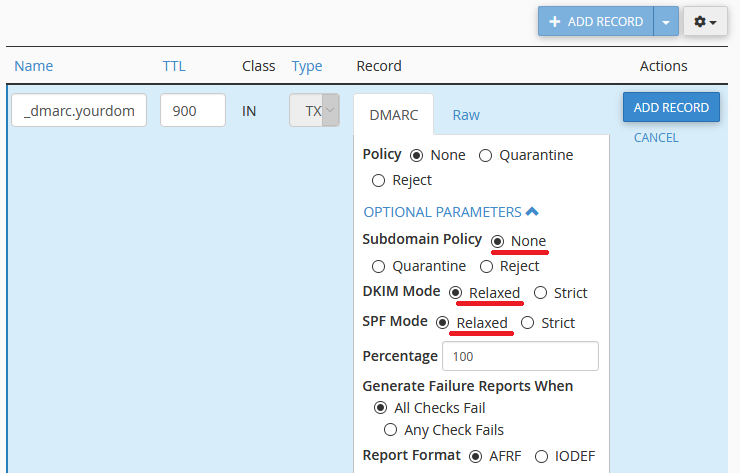
Subdomain Policy: Set how the DMARC record applies to email accounts with subdomains.
DKIM and SPF mode: Setting either of these to Relaxed will allow the DKIM/SPF of a subdomain to pass the check if the DKIM/SPF record is for a different subdomain of the primary domain (or the primary domain itself). Setting to Strict means that the DKIM/SPF must match the exact DKIM/SPF of the specific subdomain.
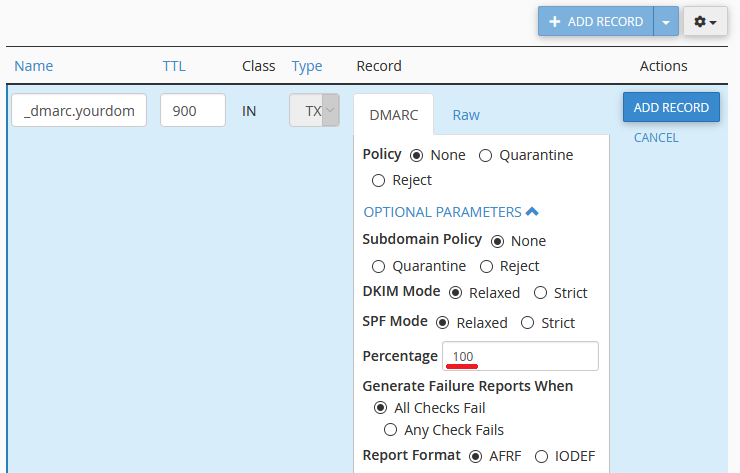
Percentage: Sets the percentage of emails which DMARC will check. It’s best to leave this at 100.
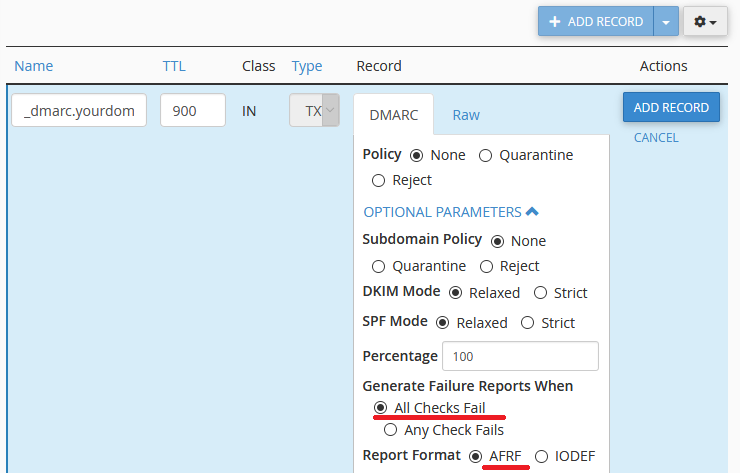
Generate Failure Reports When: Sets which emails are included in the DMARC failed emails. Select All Checks to only include emails that fail all SPF/DKIM checks. Select Any Check to include emails that fail some, but pass other checks.
Report Format: It’s best to select ARFR here as it has been specifically designed for DMARC reports.
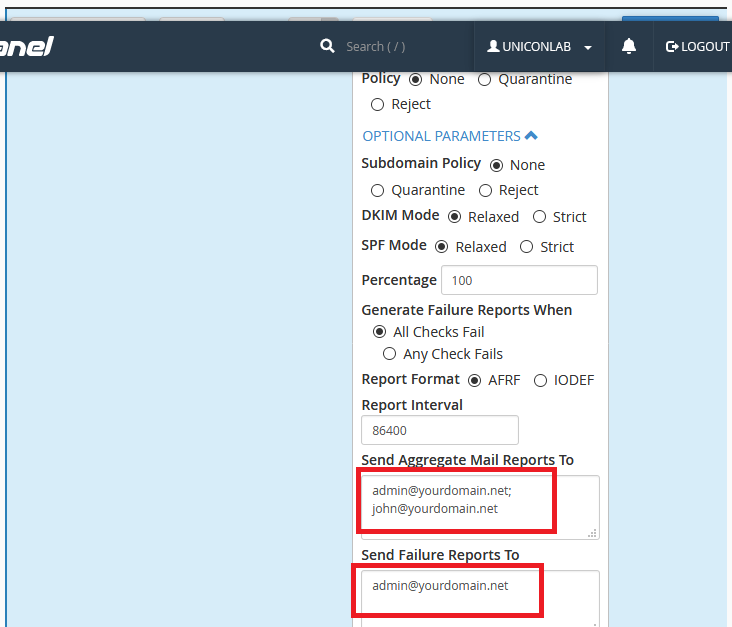
Report Interval: Sets how often a report is sent (86400 seconds is default, which is 24hrs).
Send Aggregate Mail Reports To: Set which email accounts receive complete DMARC reports (including success, failures and partial failures).
Send Failure Reports To: Set which email accounts receive reports of emails which failed DMARC.
Now click Add Record to update the configuration. And you are done.